Thoracic osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease of the thoracic spine. First of all, the disease affects the intervertebral discs, which leads to back pain and unpleasant symptoms. Also specific to the disease is the premature "aging" of the cartilage tissue of the disc.
Osteochondrosis can be diagnosed both at the age of 20 and in middle-aged patients.
The disease is less common than other forms of osteochondrosis - cervical and lumbar. This is explained by less mobility of the chest region, as well as by the protection of the muscular corset and ribs.
There are 12 vertebrae in the thoracic region - from T1 to T12. The lower vertebrae are most often affected - T10, T11, T12.
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine include:
- Chest pain
- Labored breathing
- Increased pain when taking a deep breath
- Increased fatigue
- Unsteady gait
- Feeling of tightness in the chest area
- Sluggish
- Appearance of shortness of breath
- Cold feet
- Pain in the esophagus
- cough
Pain due to thoracic osteochondrosis is divided according to its characteristics into dorsago or dorsalgia.
Dorsago - sharp pain in the chest area. It happens when you stay in one position for a long time. The pain can make breathing difficult.
Dorsalgia is moderate pain in the area of the affected discs. When you take a deep breath, the pain intensifies. Unpleasant sensations begin gradually.
Causes of the development of thoracic osteochondrosis
The causes of the appearance and development of thoracic osteochondrosis are often related to the patient's lifestyle and uneven load on the back. For example, people who spend a long time in a sitting position are at risk: remote or office work on the computer, frequent driving.
A sedentary lifestyle disrupts the functioning of the circulatory and lymphatic systems, and insufficient exercise weakens muscle tissue. At the same time, the load on the spine in a sitting position increases.
The appearance of thoracic osteochondrosis can also be influenced by previous spine injuries, excess weight and weakened immunity.
Osteochondrosis can also develop in women who often wear high heels or who are pregnant.
Aggravation of thoracic osteochondrosis is possible with an uncomfortable sleeping position, smoking, attending a poor-quality massage or hypothermia.
Complications
Degenerative processes in the thoracic spine can cause the development of the following pathologies:
- Spinal cord compression is compression of the spinal cord, which leads to decreased sensation in the abdomen, back, and chest.
- Kyphosis is a curvature of the spine.
- Spinal prolapse and herniation is a protrusion of the center of the intervertebral disc, which affects the functioning of the pancreas and intestines.
- Intercostal neuralgia - acute pain in the space between the ribs.
The organs that may be affected by the complication depend on the affected vertebra.
The rate of development of thoracic osteochondrosis
- Grade I - mild pain appears, which quickly passes in a comfortable position. Moisture is lost in the intervertebral disc and the nucleus pulposus moves slightly. This stage is not always paid attention to, because the pain does not cause severe discomfort and passes quickly.
- Grade II – cracks appear in the intervertebral disc, keeping the spine in a stable position leads to spasms, pain in the back and chest. The disc begins to lose its elasticity and its height begins to decrease. The muscles in the affected area are constantly tensed.
- Grade III - elongation of the central part of the intervertebral disc - nucleus pulposus occurs. Because of this, an intervertebral hernia occurs. The pain becomes constant and the cartilage begins to thin.
- Grade IV - the tissue of the fibrous ring is replaced by bone. Bone tissue begins to break down.
Diagnosis of thoracic osteochondrosis
If you suspect osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, you should make an appointment with a therapist or neurologist. During the examination, the patient talks about his complaints, and the doctor performs a physical examination. During the examination, attention is paid to the relationship between the levels of the shoulder girdle and the pelvis, the posture, the shape of the chest and the state of the muscular system.
After that, the doctor issues a referral for a diagnostic test. From studies, patients can be prescribed:
- X-rays – X-rays are taken in problem areas of the spine, which show changes in the discs.
- CT scan - allows you to assess the condition of the lesion site and examine the condition of the discs.
- ECG – recommended if cardiovascular disease is suspected.
How to treat thoracic osteochondrosis
For the treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, conservative methods are used. They are aimed at eliminating pain, relieving spasms and normalizing blood circulation. This includes:
- Massage
- Physiotherapy
- Physiotherapy
- Taking vitamins and medications
Massage for thoracic osteochondrosis
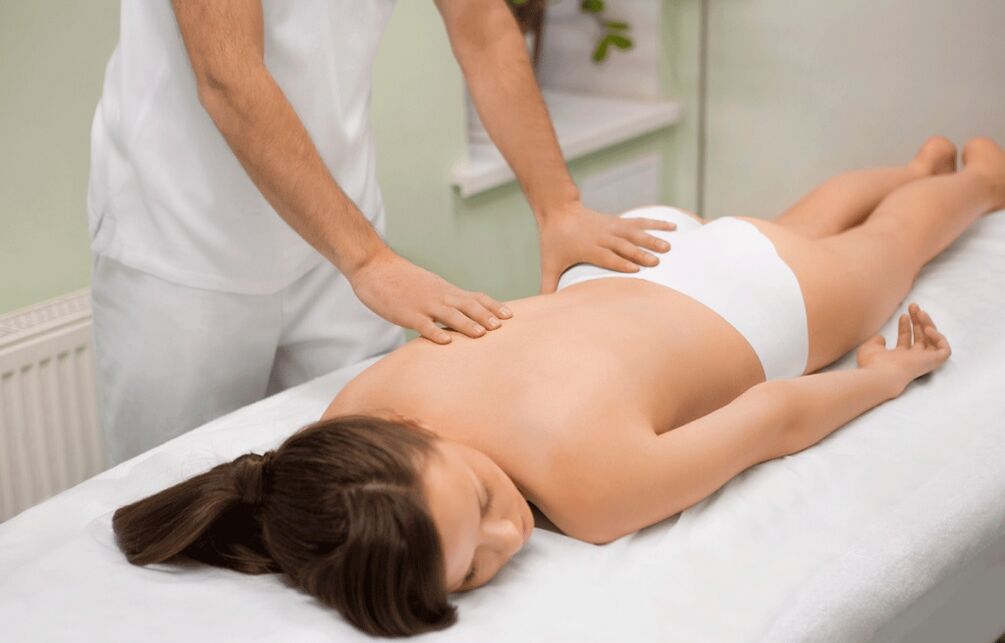
Massage of the cervical area will help relieve pain and inflammation, as well as strengthen the muscles that keep the vertebrae in a stable state.
During the session, the following massage techniques are used: hitting, squeezing, kneading, rubbing and vibration. The direction of the impact on osteochondrosis depends on the location of the lesion. The massage should be performed by a specialist who will make the procedure really effective. For greater results, special oils can be used when massaging.
However, before taking a massage course, you should make sure that it is not contraindicated for the patient. To do this, you should consult your doctor. The list of contraindications includes cardiovascular pathologies, elevated body temperature, tuberculosis and skin diseases.
Physiotherapy
Gymnastics for thoracic osteochondrosis consists of a set of exercises to strengthen the muscles of the spine and form a strong muscular corset. In the initial stages, gymnastics will help you avoid taking medications.
What effect does exercise therapy have on thoracic osteochondrosis?
- Deep breathing becomes precise
- The right attitude is formed
- Reduces the load on the spine
- The deep back muscles become less rigid
- Increases chest mobility
Exercises for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
Before starting gymnastics, you need to warm up. It can warm up and prepare the muscles for physical activity. To warm up, you can use swings of the limbs, rotations and twists of the torso, neck and pelvis.
Here are some exercises that are suitable for the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis:
- "Boat" - you need to lie on your stomach, stretch your arms above your head and keep your legs straight. In this position, you need to bend your chest - raise it smoothly and simultaneously raise your arms and legs.
- Shoulder Shrug – While standing with your arms relaxed along your body, you should lift each shoulder in turn.
- Leans on a chair - you need to sit on a chair so that your back is firmly pressed against the back. Hands should be lowered. In this position, while breathing, you should put your hands behind your back and lean back. As you exhale, you should lean forward. You can also lean to the side.
- Back arch - standing on all fours, you need to arch your back and hold this position for a few seconds. Then you need to return to the starting position. The exercise is recommended to be performed on a special mat.
The exercises should be performed regularly for several months. Therapeutic gymnastics should not last more than 30 minutes and should be done in comfortable shoes and clothes. If acute pain occurs, you should stop exercising.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is suitable for complex treatment. It can be used as an additional or independent therapy. For thoracic osteochondrosis, the doctor may prescribe the following procedures:
- Magnetotherapy is the effect of a magnetic field on the affected area, which allows you to normalize blood circulation, restore the affected tissues and improve the mobility of the lumbar region.
- Laser therapy is the effect of laser rays on the affected area. It helps improve immunity, provides analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. There is no pain during the procedure.
- Shock wave therapy is exposure to infrasonic acoustic waves. They promote the resorption of bone growth, stimulate collagen production and improve blood circulation.
- Medicinal electrophoresis is an effective technique for eliminating pain and improving nutrition of affected tissues. Electrodes and pads containing medicinal substances are attached to the patient's skin.
All these procedures will help relieve the unpleasant sensations of the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis.
%20and%20damaged%20due%20to%20thoracic%20osteochondrosis%20(red).jpg)
Drug treatment of osteochondrosis
With drug treatment, the patient is often prescribed a complex of drugs. The doctor determines the duration of the course and the list of specific drugs depending on the clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis. The list of drugs may include, for example, anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, vitamins, as well as special ointments or gels.
Nutrition for thoracic osteochondrosis
As an additional treatment measure, the patient can be prescribed the "Table No. 15" diet. The diet does not require giving up most of the popular foods, but its specialty is a diet with a high vitamin content.
As part of the diet you can eat:
- Bread
- milky
- soups
- Lean meat - it is recommended to eat it every day
- pasta
- Vegetables - fresh and in salad or cooked
- egg
- Fresh fruits
- Fresh berries
- Many types of sweets
- Butter and vegetable oils
Allowed drinks include weak coffee, tea, juices and kvass.
What you should not eat:
- Desserts with nuances
- Dishes with fatty meat or fish
- Chocolate products
As for drinks, it is not recommended to drink strong coffee, strong tea or alcoholic beverages.
Prevention of thoracic osteochondrosis
Recommended preventive measures include:
- Swimming or other water sports
- Regular heating when working on the computer for a long time
- Keeping the posture in a sitting position - the back should be straight and the shoulders should be straightened
- Avoiding back hypothermia
- Regular exercise therapy
In addition, attention should be paid to the choice of bed. An ill-fitting mattress and pillow will prevent your back and neck from relaxing during sleep. For this reason, for a comfortable stay with osteochondrosis, it is recommended to purchase special orthopedic equipment.

















































