As a person ages, the risk of developing diseases of the spine and joints increases. This is due to degenerative and destructive changes in the body. One of the common pathologies is arthrosis of the ankle joint.
Osteoarthritis of the ankle joint - what is it?
Ankle arthrosis is a chronic disease and cannot be completely cured. According to statistics, 10% of people have this dystrophic disorder. People over 40 are especially susceptible to it. The disease can lead to disability. Therefore, it should be handled promptly and competently.
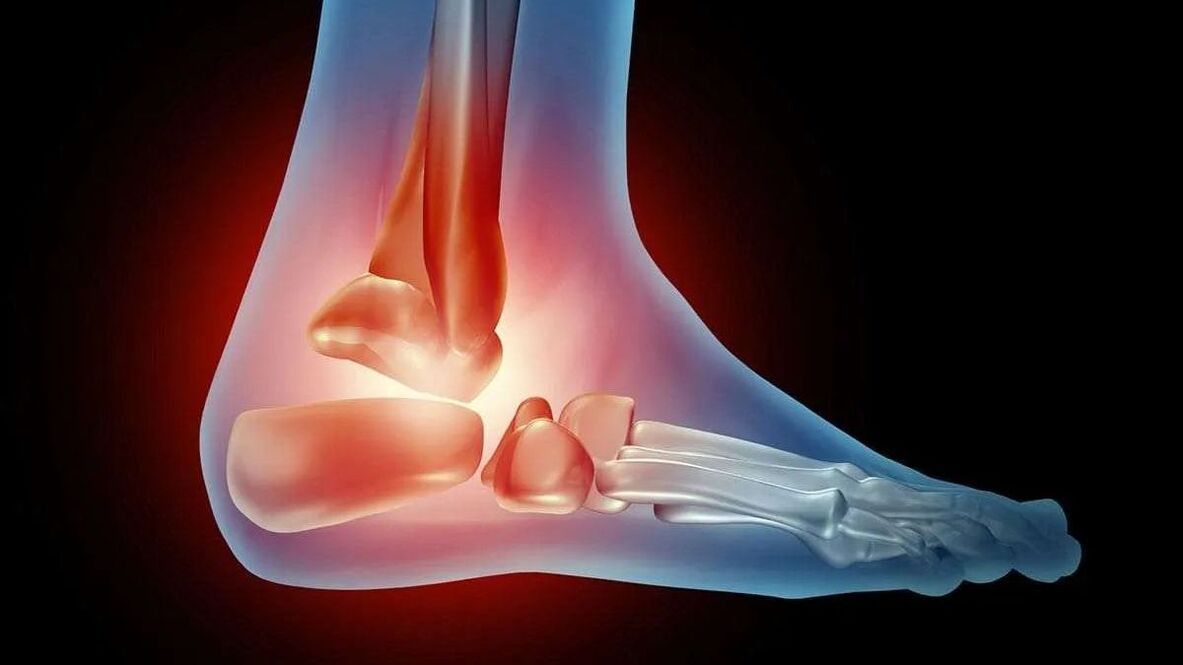
The ankle consists of the fibula, tail and tibia, two malleolus and articular ligaments. With arthrosis, inflammation and destruction of articular cartilage occurs. Bone tissue is damaged and deformed as the pathology progresses.
ICD 10 code
ICD stands for International Classification of Diseases. In such a document, each disease is assigned a specific code. This code consists of letters and numbers and is indicated on the sick leave certificate when you make a diagnosis. Thanks to it, a doctor in any country will understand what the patient is suffering from and where the pathological focus is located.
The diagnosis of arthrosis is presented in a block of 5 headings and several subheadings. Osteoarthritis of the ankle is included in category M19. This section is divided into 5 subsections. The sign after the dot indicates the etiology. So, 0 - these are genetically determined degenerative changes, 1 - post-traumatic changes, 2 - dystrophic changes against the background of endocrine, vascular or inflammatory pathology, 8 - these are other specified causes, 9 - a disease due tounknownFor example, code M19. 1 is ankle arthrosis resulting from injury.
Causes
Pathology develops for various reasons. Provocative factors for the appearance of the disease in adults are:
- Increased load on joints. Doctors often observe degenerative changes in cartilage and bone tissue in obese patients and professional athletes (football players, bodybuilders, runners and dancers).
- Diabetes.
- Ankle injury.
- Wearing uncomfortable shoes, walking in heels.
In children, pathology develops for the following reasons:
- Thyrotoxicosis.
- Tissue dysplasia.
- The injury.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Fracture.
- Inflammation of the joints.
- Dislocation.
Symptoms
The following manifestations are typical for ankle arthrosis:
- Pain. Appears after standing in a position. When a person tries to stand up and lean on his leg, he experiences stabbing pain and stiffness of movement. After a few steps, the discomfort goes away. Pain appears during and after physical activity.
- Clicking, popping in the ankle joint while walking.
- Restriction of movements.
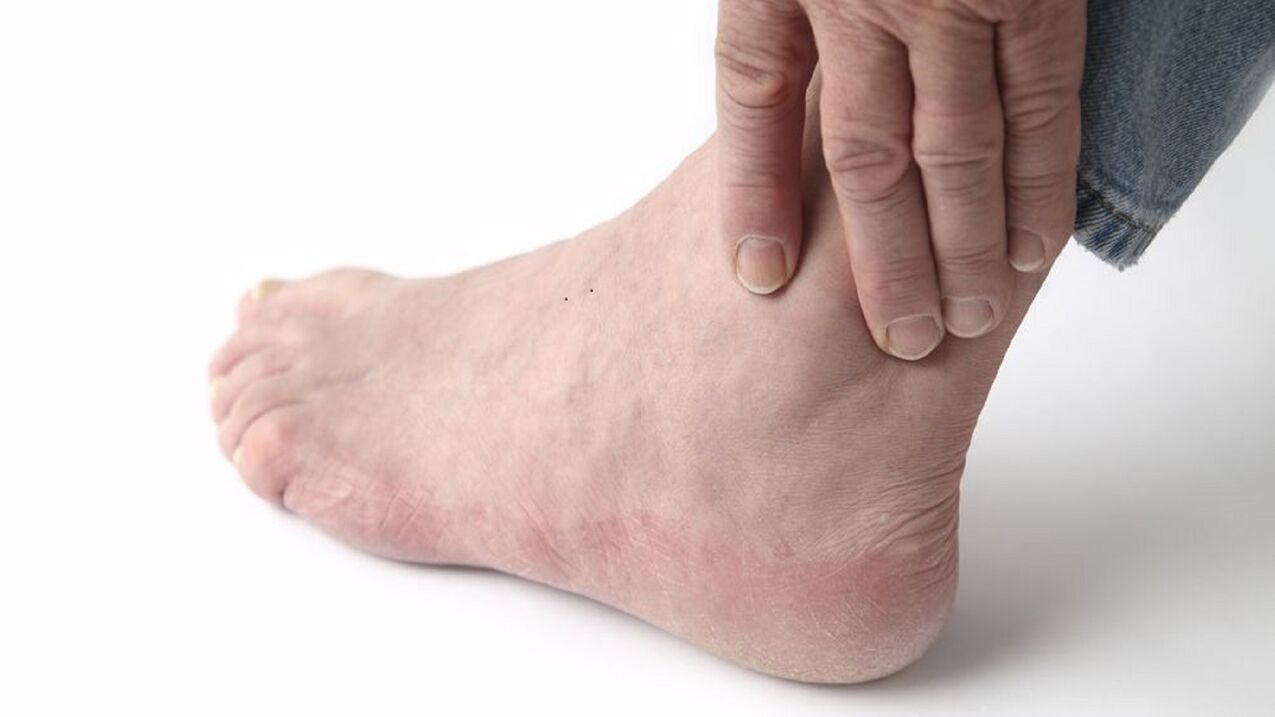
- Swelling under the ankle.
- Hypotrophy, weakness of the ligamentous apparatus.
- Deformation of the joint (typical of an advanced disease).
Diplomas
There are several degrees of arthrosis. Many years pass from the appearance of the first signs of degenerative changes in the joints to the loss of mobility. If you start therapy in time, there is a chance to stop the progression of the disease. The success of the treatment depends on the stage at which the pathology was detected.
Degrees of arthrosis of the ankle joint:
- First. The degenerative process has just begun to develop and does not cause much concern to a person. The only symptoms are temporary morning stiffness in the legs, fatigue and mild pain. When you bend and straighten your leg, there is a clicking sound. No pathological changes are detected on x-ray. The prognosis for drug treatment is favorable.
- Secondly. The symptoms of the disease intensify. Morning stiffness does not go away for about an hour. Pain appears at the beginning of walking. Having covered only 1 km distance, a person feels very tired on foot. When the ankle moves, there is a clicking sound. X-rays show osteophytes, the convergence of the ends of the bones. Surgical treatment is indicated.
- Third. The pain syndrome occurs not only during movement, but also at rest. A person cannot work or rest normally without anesthetics. The patient is unable to move independently. X-ray image shows cracks, flattening of joint surfaces, osteophytes and subluxation. Treatment is surgical and medicinal.
- Fourthly. The manifestations of the disease are mild. The pain goes away. But the stiffness of the movement does not allow a person to walk. The cartilage in the fourth stage is completely destroyed. X-ray shows healing of the key space.
Diagnosing
During the diagnosis, the doctor determines the degree of the disease and identifies the deterioration. Laboratory and hardware techniques are used for this:
- Blood test (detailed).
- Rheumatoid tests.
- Ultrasound.
- CT.
- CRP test.
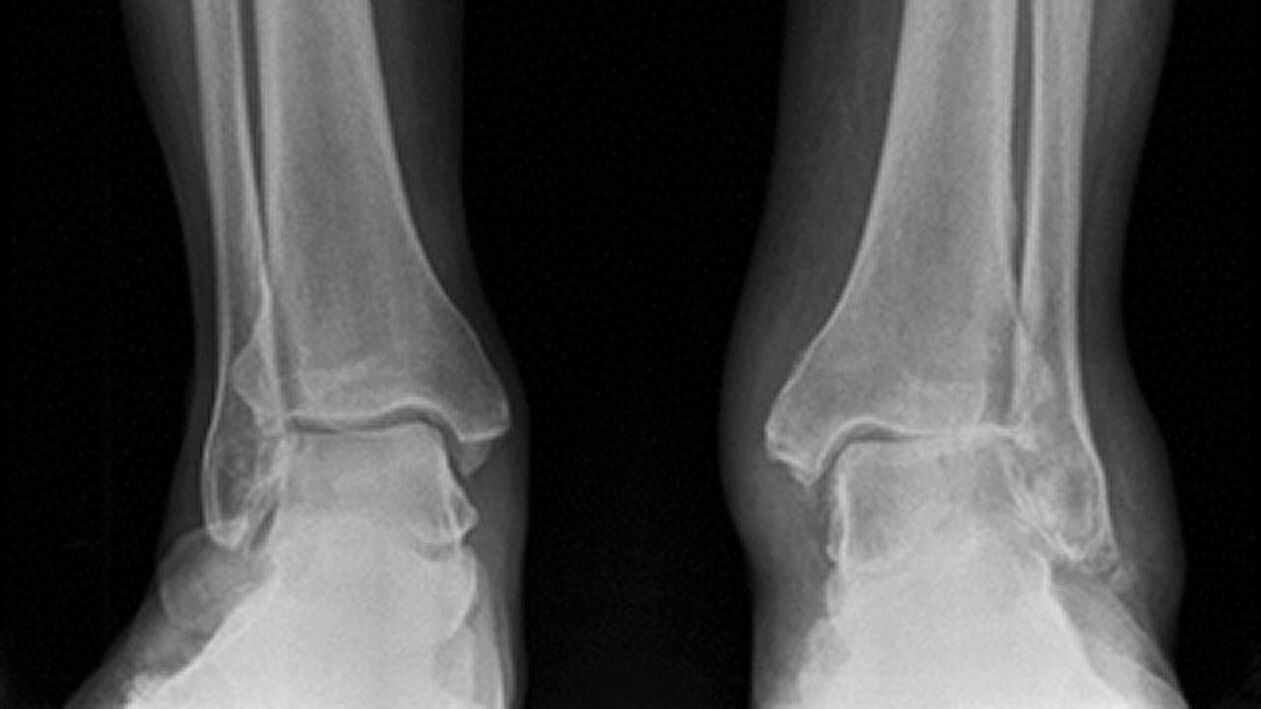
- Radiography.
- MRI.
Treatment
Therapy should be comprehensive and include taking medications, using physical therapy methods, and performing therapeutic physical exercises.
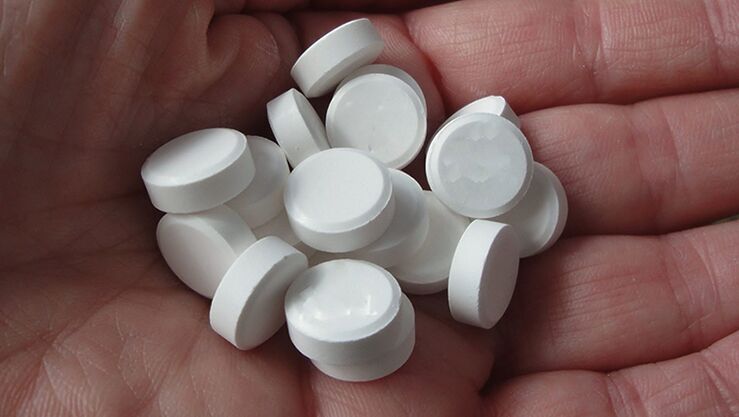
The patient is prescribed the following drugs:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Chondroprotectors.
- Painkillers.
- Corticosteroid hormones.

Joint mobility is restored with manual therapy and procedures using a special apparatus. Physiotherapy accelerates regeneration and stimulates blood circulation in the affected joint. Electrical stimulation, laser therapy and ultrasound are effective. In case of marked dystrophic changes, endoprosthetics are performed.
Preventing
You can prevent ankle arthrosis by following the following rules:
- Keep your weight within normal limits.
- Strengthen the spine with special exercises.
- Avoid injuries.
- Correct congenital anomalies of joint structure.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Treat endocrine and vascular disorders in a timely manner.
- Regularly perform preventive examinations if you have a genetic predisposition to the disease.

















































